Q: What are the different types of electric relays?
…
A: An electric relay is a high amperage switch controlled with a small electrical input. Normally, the small input controls an electromagnetic coil. This coil moves a set of contacts which can handle between 10 to 200 amps.
Relay Terms & Schematics explained
Relays are usually printed with voltage, amperage, and a numbered diagram showing how they work. The diagram shows the contacts in the normal position. This is when the coil is not energized.
The numbers will match the terminals or “pins” on the relay.
Single Pole Relays
Single pole relays have one output terminal for each throw of the contact.
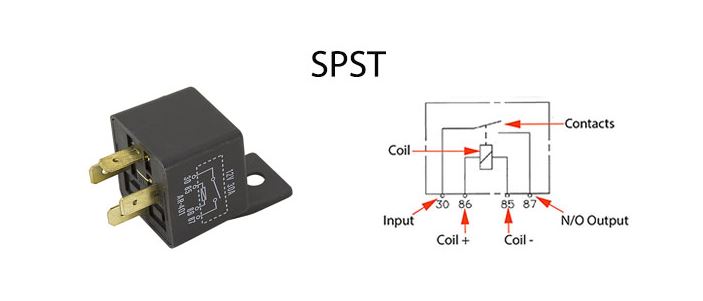
Standard four-pin single pole, single throw (SPST) relays have one normally open (N/O) output terminal.
When the coil is energized, it throws the contact. This completes the circuit between the common pin 30 and pin 87. In the normal position, this circuit is open.
- For more information, watch this: How to wire a relay.
…
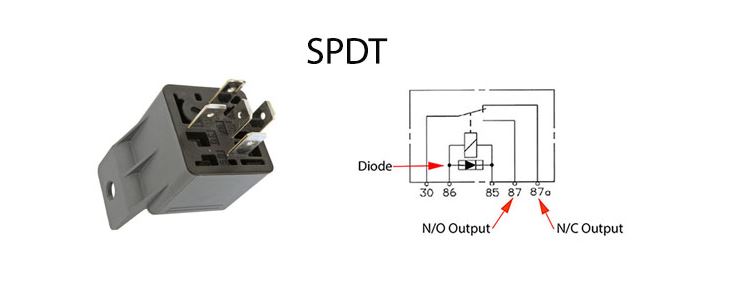
Standard five-pin single pole, double throw (SPDT) relays have one N/O and one normally closed (N/C) output terminal.
When the contact is thrown, pin 87 is connected to pin 30 just like the SPST relay. In the normal position, the contact is thrown back and pin 87a is connected to pin 30.
- A SPDT relay can be used in place of a N/O or N/C SPST relay by connecting to only one output terminal.
…
Double Pole Relays
Double pole (DP) relays have two output terminals for each throw of the contact. DP relays are uncommon. Two standard single pole relays with shared coil control are often used instead.
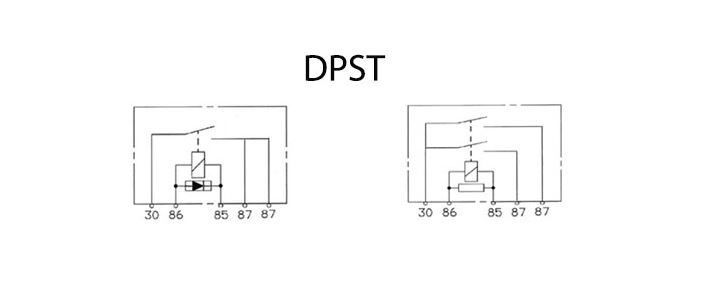
DPST relays look like SPDT relays from the outside.
Both relays have five pins. You have to look at the diagram to tell them apart. Both output terminals (87) are connected to pin 30 when the coil is energized.
- Some manufacturers refer to these five-pin relays as SPST with two N/O outputs.
…
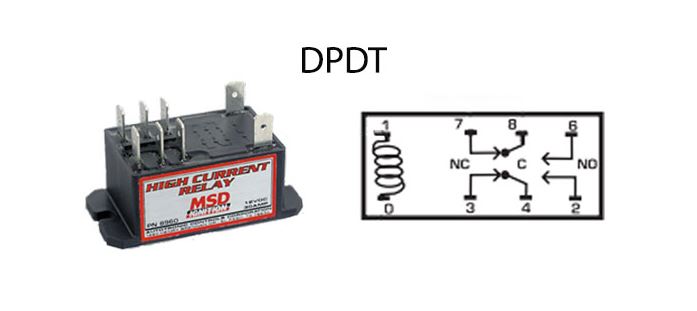
There’s no mistaking DPDT relays for anything else. They have eight pins, two N/O outputs, and two N/C outputs. Even though the diagram looks different, we can still tell how this relay works.
What are the Benefits of Using a Relay?
Keeping high-amperage wiring as short as possible reduces voltage drop. This makes your devices run better and saves on installation costs.
Relays allow you to control high-amperage devices with a light-duty switch or a low-amperage signal from an electronic module.
- Relays with a diode inside protect electronic modules from voltage spikes.
…
This is another in a series of weekly Q&A Mailbag sessions with the Summit Racing tech department, in which there are hundreds more. Click here to see them all.

Do you know of a simple, single-page pdf (or whatever) of all these with simple instructions on what each pin is? Thanks!
Check out this article.
[…] Q: What are the different types of electric relays? … A: An electric relay is a high amperage switch controlled with a small electrical input. Normally, the small input controls an electromagnetic […] Read full article at http://www.onallcylinders.com […]